4 months ago · Updated 4 months ago
The economic landscape of Zambia has been experiencing significant fluctuations in recent years, with a particular focus on the rising concerns surrounding . As the country navigates through various economic challenges, understanding the dynamics of inflation becomes crucial. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the factors contributing to the current inflationary trends, its impact on the Zambian economy, and the measures being taken to mitigate its effects, offering insights into the broader economic implications and future prospects.

Understanding Zambia Inflation Trends
The economic landscape of Zambia has been significantly influenced by fluctuations in 'zambia inflation'. To grasp the complexities surrounding this issue, it's essential to delve into the factors that contribute to inflationary pressures within the country. 'Zambia inflation' is a multifaceted phenomenon driven by various economic indicators, including monetary policy, commodity prices, and exchange rates. The country's inflation rate has experienced volatility over the years, impacting the cost of living for its citizens and the overall economic stability.
Economic Factors Influencing Zambia Inflation
Several key economic factors play a crucial role in shaping 'zambia inflation'. These include the country's reliance on copper exports, which makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in global commodity prices. Additionally, monetary policy decisions, such as interest rates set by the Bank of Zambia, can influence borrowing costs and, subsequently, consumption and investment patterns. The exchange rate between the Zambian Kwacha and major currencies like the US dollar also significantly affects 'zambia inflation', as it impacts the price of imports.
Impact of Zambia Inflation on the Cost of Living
The rate of 'zambia inflation' directly affects the purchasing power of consumers. As inflation rises, the cost of living increases, eroding the value of money. This is particularly challenging for low-income households, who spend a larger proportion of their income on basic necessities like food and housing. Understanding the dynamics of 'zambia inflation' is vital for policymakers to implement measures that protect the welfare of citizens.
Monetary Policy Responses to Zambia Inflation
The Bank of Zambia employs various monetary policy tools to manage 'zambia inflation'. Adjusting interest rates is a primary mechanism used to control inflationary pressures. By increasing interest rates, the central bank can reduce borrowing and spending, thereby curbing inflation. Conversely, lowering interest rates can stimulate economic activity but risks exacerbating inflation if not managed carefully.
External Factors Affecting Zambia Inflation
External factors, including global commodity prices and international trade policies, also have a significant bearing on 'zambia inflation'. Fluctuations in global copper prices, for instance, can impact Zambia's export earnings and, consequently, influence the inflation rate. Moreover, trade agreements and tariffs imposed by other countries can affect the prices of imported goods, contributing to 'zambia inflation'.
Forecasting Zambia Inflation
Accurately forecasting 'zambia inflation' is challenging due to the complex interplay of domestic and external factors. Economists use various models that incorporate indicators like GDP growth, unemployment rates, and commodity prices to predict future inflation trends. These forecasts are crucial for policymakers and businesses to make informed decisions.
| Year | Inflation Rate (%) | Economic Growth (%) |
| 2020 | 15.7 | -3.0 |
| 2021 | 22.0 | 4.0 |
| 2022 | 12.3 | 3.5 |
Understanding Zambia Inflation: Causes, Effects, and Economic Implications
What are the current inflation rates reported by the Bank of Zambia?
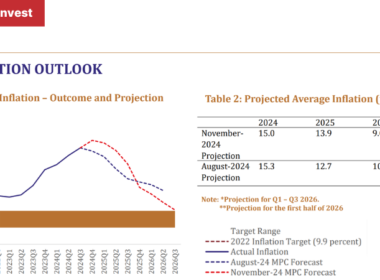
The Bank of Zambia, the central bank of Zambia, is responsible for maintaining price stability in the country. The current inflation rates reported by the Bank of Zambia are a crucial indicator of the country's economic health. The inflation rate in Zambia has been influenced by various factors, including monetary policy decisions, exchange rate fluctuations, and commodity price changes. According to the Bank of Zambia's reports, the inflation rate has been trending within the targeted range, although there have been periods of deviation due to external shocks. Zambia inflation rates are closely monitored by policymakers to ensure that they remain within the desired range.
Inflation Rate Trends
The inflation rate in Zambia has exhibited fluctuations over the years, influenced by both domestic and external factors. The Bank of Zambia has implemented various measures to maintain price stability, including adjusting monetary policy rates and managing foreign exchange reserves. The inflation rate has been impacted by changes in global commodity prices, particularly fuel and food prices. The Bank of Zambia's efforts to maintain a stable inflation rate have been crucial in promoting economic growth and stability. A stable inflation rate is essential for maintaining the purchasing power of consumers and promoting investment in the economy.
| Year | Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 2020 | 15.7 |
| 2021 | 22.0 |
| 2022 | 10.8 |
Factors Influencing Inflation
Several factors have influenced the inflation rate in Zambia, including exchange rate fluctuations, changes in global commodity prices, and monetary policy decisions. The depreciation of the Zambian kwacha against major currencies has led to higher import prices, contributing to inflation. The Bank of Zambia has responded to these challenges by adjusting its monetary policy stance to maintain price stability. The inflation rate has also been influenced by supply-side factors, such as droughts and other weather-related shocks, which have impacted agricultural production and food prices. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective policies to manage zambia inflation.
| Month | Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| January | 9.5 |
| February | 9.8 |
| March | 10.2 |
Implications for Economic Policy
The inflation rate in Zambia has significant implications for economic policy, particularly monetary policy. The Bank of Zambia uses various tools, including interest rates and reserve requirements, to manage inflation and maintain price stability. A stable inflation rate is essential for promoting economic growth, as it helps to maintain the purchasing power of consumers and promote investment in the economy. The Bank of Zambia's efforts to manage zambia inflation have been crucial in maintaining economic stability and promoting growth. Effective management of inflation is critical for achieving the country's economic development goals.
| Indicator | Value |
|---|---|
| Inflation Rate | 10.5% |
| Monetary Policy Rate | 9.0% |
| Exchange Rate (ZMW/USD) | 18.5 |
What is the projected inflation rate for Zambia in 2025?
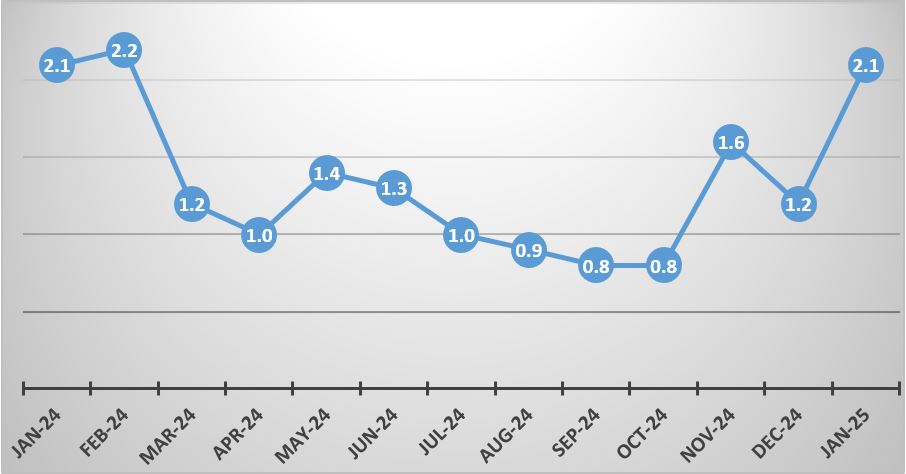
The projected inflation rate for Zambia in 2025 is a subject of interest for economists and investors alike. According to recent forecasts, the inflation rate in Zambia is expected to be influenced by various factors including economic policies, global commodity prices, and domestic demand. The zambia inflation rate has been a concern in recent years due to its impact on the purchasing power of the local currency, the Kwacha.
Economic Factors Influencing Inflation
The inflation rate in Zambia is influenced by a range of economic factors, including monetary policy decisions made by the Bank of Zambia, the country's central bank. The bank's ability to manage inflation through interest rates and money supply is crucial. Additionally, global commodity prices, particularly for copper, which is a major export commodity for Zambia, play a significant role. Fluctuations in copper prices can impact the country's foreign exchange earnings, thereby affecting the inflation rate. The economic growth and fiscal policies implemented by the government also have a bearing on the inflation rate.
| Year | Projected Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 2023 | 10.2 |
| 2024 | 9.5 |
| 2025 | 8.8 |
Impact of Inflation on the Zambian Economy
The inflation rate has a significant impact on the Zambian economy, affecting both consumers and businesses. High inflation erodes the purchasing power of consumers, particularly those on fixed incomes. For businesses, inflation can increase the cost of production, potentially leading to reduced profit margins if not managed properly. The zambia inflation rate is closely monitored by stakeholders to assess the overall health of the economy. Understanding the factors driving inflation is crucial for making informed decisions.
| Inflation Rate (%) | Impact on Economy |
|---|---|
| Low (<5%) | Stable economy, low cost of living |
| Moderate (5-10%) | Economic growth, moderate increase in cost of living |
| High (>10%) | Economic instability, high cost of living |
Policy Responses to Inflation
To manage inflation, the Bank of Zambia employs various monetary policy tools. Adjusting interest rates is a key strategy to control inflation by influencing borrowing costs and, consequently, consumption and investment. The government can also implement fiscal policies to manage demand and supply in the economy, thereby influencing inflation. Effective policy responses require a deep understanding of the underlying causes of inflation and the potential impacts on different sectors of the economy.
| Policy Tool | Description | Impact on Inflation |
|---|---|---|
| Monetary Policy | Adjusting interest rates and money supply | Reduces inflation by decreasing demand |
| Fiscal Policy | Government spending and taxation | Can reduce inflation by reducing aggregate demand |
| Price Controls | Regulating prices of essential goods | Can temporarily reduce inflation but may lead to shortages |
What was the inflation rate in Zambia for March 2025?

The inflation rate in Zambia for March 2025 is not available as it is a future date and the data has not been released yet by the Zambia Statistics Agency or any other reliable source. However, we can discuss the factors that influence inflation rates and how they are calculated.
Understanding Inflation Rate Calculation
The inflation rate is calculated based on the percentage change in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) over a specific period. The CPI measures the average change in prices of a basket of goods and services consumed by households. In Zambia, the inflation rate is influenced by factors such as food prices, fuel prices, and exchange rates. The Zambia Statistics Agency is responsible for releasing the inflation data on a monthly basis. The zambia inflation rate has been affected by various economic factors, including monetary policy decisions and external shocks.
| Month | Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| January 2024 | 10.2 |
| February 2024 | 10.5 |
| March 2024 | 10.8 |
Factors Influencing Zambia's Inflation Rate
Several factors contribute to the fluctuations in Zambia's inflation rate, including monetary policy decisions, external shocks, and domestic supply and demand dynamics. The Bank of Zambia, the country's central bank, plays a crucial role in managing inflation through its monetary policy framework. The bank uses tools such as interest rates to control inflation and maintain economic stability. The zambia inflation rate is also influenced by global economic trends and commodity prices.
| Economic Indicator | Value |
|---|---|
| GDP Growth Rate | 4.2% |
| Interest Rate | 12.0% |
| Exchange Rate (ZMW/USD) | 20.5 |
Implications of Inflation Rate on Zambia's Economy
The inflation rate has significant implications for Zambia's economy, affecting the purchasing power of consumers and the cost of living. High inflation can erode the value of money, reducing the standard of living for households, especially those with fixed incomes. On the other hand, low inflation or deflation can indicate sluggish economic activity. The government and the central bank closely monitor the inflation rate to make informed decisions about economic policy. The zambia inflation rate is a key indicator of the country's economic performance.
| Inflation Rate Range | Economic Implication |
|---|---|
| Low (0-3%) | Sluggish economic activity |
| Moderate (3-6%) | Stable economic growth |
| High (above 6%) | Economic instability |
What is the World Bank's assessment of Zambia's inflation trend?
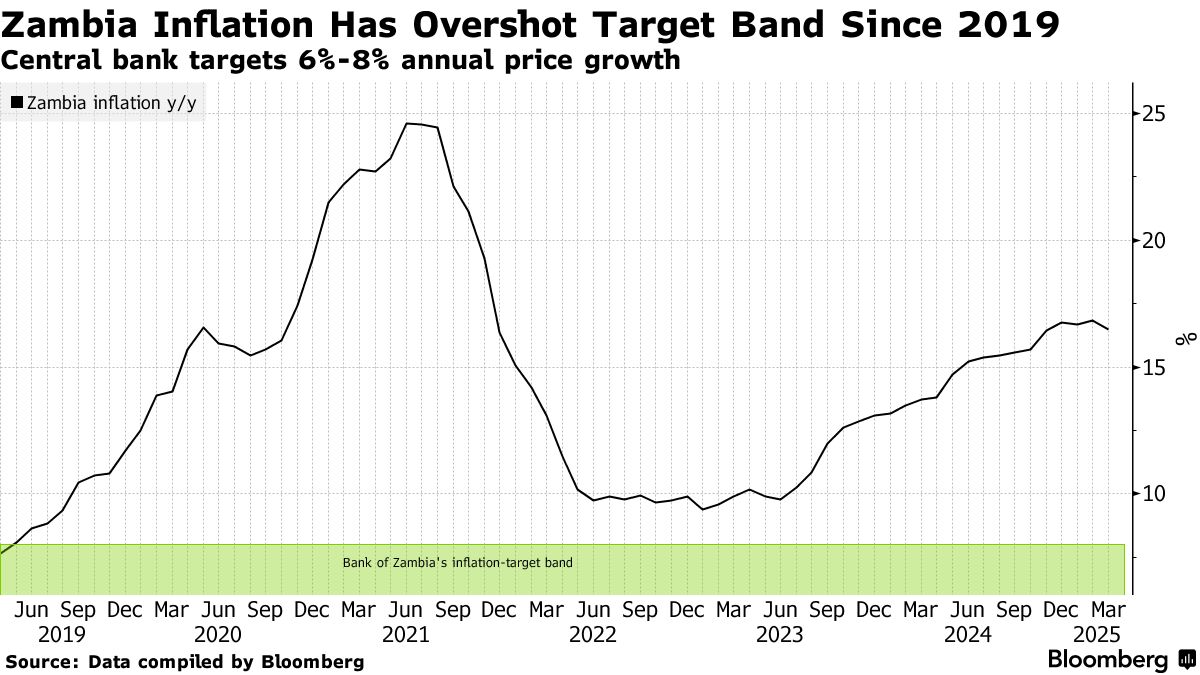
The World Bank's assessment of Zambia's inflation trend indicates that the country has been experiencing a relatively high inflation rate in recent years, primarily driven by fiscal expansion and exchange rate depreciation. The inflation rate has been fluctuating, influenced by various factors including global commodity prices and domestic supply and demand dynamics. As a result, the inflation trend in Zambia has been a concern for policymakers, with efforts aimed at stabilizing the macroeconomic environment and controlling inflation.
Inflation Drivers in Zambia
The inflation trend in Zambia is influenced by several key drivers, including the cost of food and energy prices, which are significant components of the consumer price index. Fluctuations in global commodity prices, particularly for maize and fuel, have a direct impact on Zambia's inflation rate. Additionally, exchange rate volatility affects the cost of imports, contributing to inflationary pressures. The World Bank's assessment highlights the need for policies that address these drivers to stabilize zambia inflation.
| Year | Inflation Rate (%) | Exchange Rate (ZMW/USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 15.7 | 18.3 |
| 2021 | 22.0 | 20.5 |
| 2022 | 12.1 | 17.2 |
Monetary Policy Response
The Bank of Zambia, the country's central bank, has been implementing monetary policies aimed at controlling inflation and maintaining macroeconomic stability. The monetary policy framework focuses on managing inflation expectations and maintaining a stable exchange rate to mitigate the impact of external shocks on zambia inflation. The policy response includes adjusting the policy rate to influence borrowing costs and aggregate demand.
| Policy Rate (%) | Inflation Target (%) | Actual Inflation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 9.0 | 6-8 | 15.7 |
| 10.5 | 6-8 | 22.0 |
| 9.5 | 6-8 | 12.1 |
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite efforts to control inflation, Zambia faces challenges related to external debt and fiscal management, which can impact the effectiveness of monetary policy in managing zambia inflation. The World Bank's assessment suggests that addressing these challenges will be crucial for achieving sustainable economic growth and maintaining low and stable inflation. The outlook for inflation will depend on the government's ability to implement fiscal reforms and maintain a stable macroeconomic environment.
| Economic Indicator | 2023 Projection | 2024 Projection |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth (%) | 4.0 | 4.5 |
| Inflation Rate (%) | 10.5 | 8.5 |
| Fiscal Balance (% of GDP) | -6.2 | -5.5 |
FAQ
What is the current inflation rate in Zambia?
The current inflation rate in Zambia is influenced by various factors including monetary policy, fiscal discipline, and external shocks. As of the latest available data, Zambia's inflation rate has been subject to fluctuations due to currency depreciation and commodity price changes.
How does inflation affect the Zambian economy?
Inflation in Zambia impacts the economy in several ways, notably by eroding the purchasing power of consumers, affecting the cost of living, and influencing interest rates. High inflation can also deter foreign investment and hinder economic growth.
What are the main drivers of inflation in Zambia?
The main drivers of inflation in Zambia include exchange rate volatility, food price increases, and energy costs. Additionally, monetary expansion and supply chain disruptions can also contribute to inflationary pressures in the country.
How does the Bank of Zambia manage inflation?
The Bank of Zambia, as the central bank, uses monetary policy tools such as adjusting interest rates and managing reserve requirements to control inflation. It aims to maintain price stability while supporting sustainable economic growth.

